Congratulations to the publication of “Structural insights into the recognition of histone H3Q5 serotonylation by WDR5” in Science Advances.
Structural insights into the recognition of histone H3Q5 serotonylation by WDR5
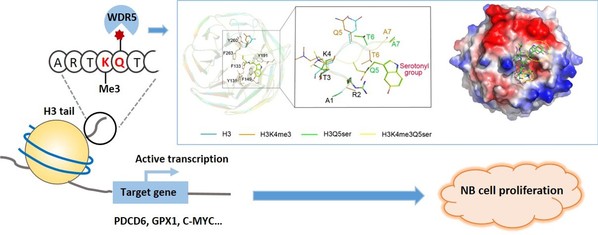
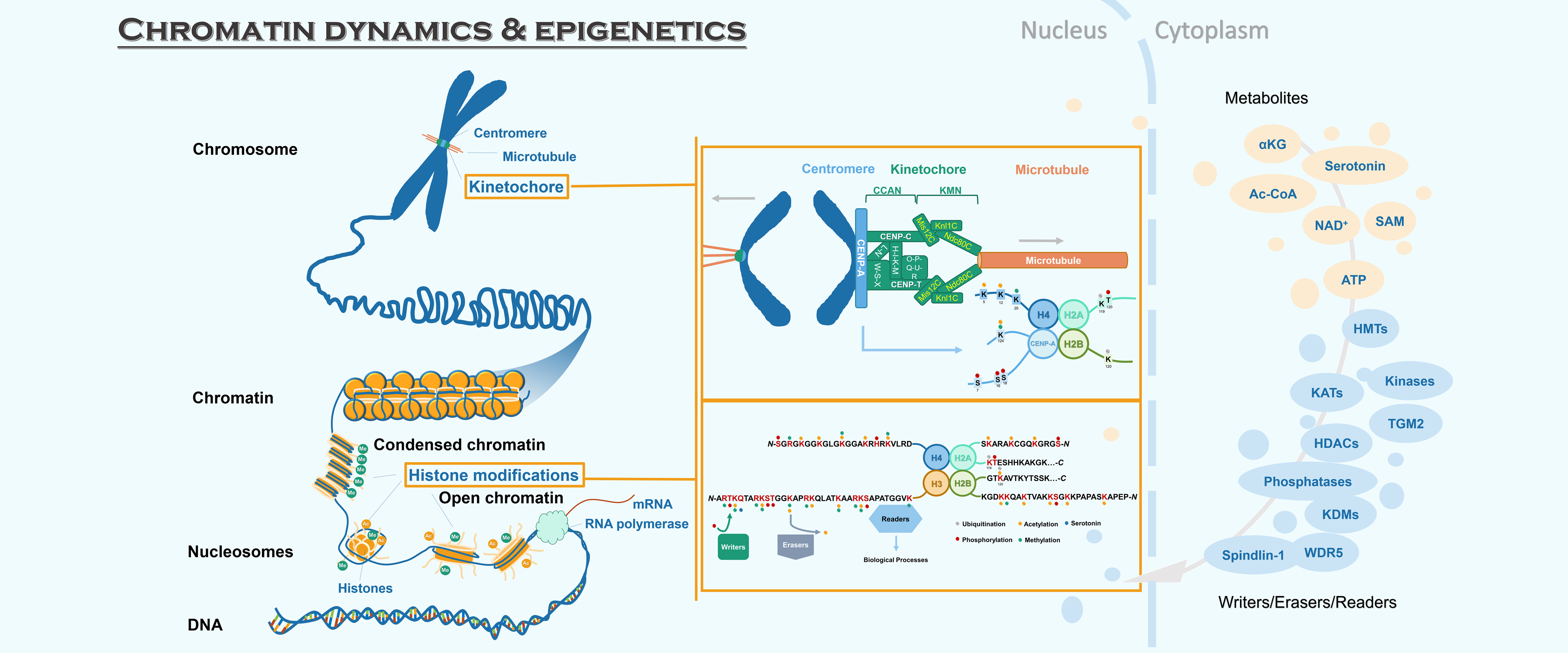
Serotonylation of histone H3Q5 (H3Q5ser) is a recently identified posttranslational modification of histones that acts as a permissive marker for gene activation in synergy with H3K4me3 during neuronal cell differentiation. However, any proteins that specifically recognize H3Q5ser remain unknown. Here, we found that WDR5 interacts with the N-terminal tail of histone H3 and functions as a “reader” for H3Q5ser. Crystal structures of WDR5 in complex with H3Q5ser and H3K4me3Q5ser peptides revealed that the serotonyl group is accommodated in a shallow surface pocket of WDR5. Experiments in neuroblastoma cells demonstrate that H3K4me3 modification is hampered upon disruption of WDR5-H3Q5ser interaction. WDR5 colocalizes with H3Q5ser in the promoter regions of cancer-promoting genes in neuroblastoma cells, where it promotes gene transcription to induce cell proliferation. Thus, beyond revealing a previously unknown mechanism through which WDR5 reads H3Q5ser to activate transcription, our study suggests that this WDR5-H3Q5ser–mediated epigenetic regulation apparently promotes tumorigenesis.
Congrats to Jie Zhao and Wanbiao Chen for their great work. This finding was published in “Science Advances” on 18 June 2021. Please see the full-text manuscript at https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-020-03502-1.